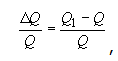-
1 instability factor
коэффициент нестабильности
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
коэффициент нестабильности магнитной величины
Отношение нестабильности магнитной величины к начальному значению магнитной величины, измеренному до воздействия механических, климатических и других внешних факторов.
[ ГОСТ 19693-74]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
- facteur d’instabilité
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > instability factor
-
2 instability factor
Техника: коэффициент нестабильности -
3 inductance instability factor of coil
коэффициент нестабильности индуктивности катушки
коэффициент нестабильности индуктивности
Отношение изменения индуктивности к произведению квадрата индуктивности в начальный период времени и логарифма отношения времен, за которые произошло это изменение.
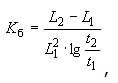
где L1 - индуктивность в начале периода времени (t1);
L2 - индуктивность в конце периода времени (t2)
[ ГОСТ 20718-75]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
FR
- coefficient d’instabilité d'inductance de bobine
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > inductance instability factor of coil
-
4 gain instability factor (for pumping)
коэффициент нестабильности усиления (по накачке)
Отношение относительного изменения коэффициента усиления квантового парамагнитного усилителя к соответствующему относительному изменению мощности накачки.
[Сборник рекомендуемых терминов. Выпуск 75. К вантовая электроника. Академия наук СССР. Комитет научно-технической терминологии. 1984 г.]Тематики
Обобщающие термины
EN
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > gain instability factor (for pumping)
-
5 gain instability factor
Макаров: коэффициент нестабильности усиленияУниверсальный англо-русский словарь > gain instability factor
-
6 gain instability factor
English-russian dictionary of physics > gain instability factor
-
7 instability of quality-factor of coil
нестабильность добротности катушки индуктивности
нестабильность добротности
Ндп. стабильность добротности
Относительное изменение добротности под воздействием различных факторов.
где Q - добротность до воздействия каких-либо факторов;
Q1 - добротность после воздействия каких-либо факторов
[ ГОСТ 20718-75]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
Синонимы
EN
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > instability of quality-factor of coil
-
8 thermal
1 adjPHYS, REFRIG, THERMO térmico2 -
9 Economy
Portugal's economy, under the influence of the European Economic Community (EEC), and later with the assistance of the European Union (EU), grew rapidly in 1985-86; through 1992, the average annual growth was 4-5 percent. While such growth rates did not last into the late 1990s, portions of Portugal's society achieved unprecedented prosperity, although poverty remained entrenched. It is important, however, to place this current growth, which includes some not altogether desirable developments, in historical perspective. On at least three occasions in this century, Portugal's economy has experienced severe dislocation and instability: during the turbulent First Republic (1911-25); during the Estado Novo, when the world Depression came into play (1930-39); and during the aftermath of the Revolution of 25 April, 1974. At other periods, and even during the Estado Novo, there were eras of relatively steady growth and development, despite the fact that Portugal's weak economy lagged behind industrialized Western Europe's economies, perhaps more than Prime Minister Antônio de Oliveira Salazar wished to admit to the public or to foreigners.For a number of reasons, Portugal's backward economy underwent considerable growth and development following the beginning of the colonial wars in Africa in early 1961. Recent research findings suggest that, contrary to the "stagnation thesis" that states that the Estado Novo economy during the last 14 years of its existence experienced little or no growth, there were important changes, policy shifts, structural evolution, and impressive growth rates. In fact, the average annual gross domestic product (GDP) growth rate (1961-74) was about 7 percent. The war in Africa was one significant factor in the post-1961 economic changes. The new costs of finance and spending on the military and police actions in the African and Asian empires in 1961 and thereafter forced changes in economic policy.Starting in 1963-64, the relatively closed economy was opened up to foreign investment, and Lisbon began to use deficit financing and more borrowing at home and abroad. Increased foreign investment, residence, and technical and military assistance also had effects on economic growth and development. Salazar's government moved toward greater trade and integration with various international bodies by signing agreements with the European Free Trade Association and several international finance groups. New multinational corporations began to operate in the country, along with foreign-based banks. Meanwhile, foreign tourism increased massively from the early 1960s on, and the tourism industry experienced unprecedented expansion. By 1973-74, Portugal received more than 8 million tourists annually for the first time.Under Prime Minister Marcello Caetano, other important economic changes occurred. High annual economic growth rates continued until the world energy crisis inflation and a recession hit Portugal in 1973. Caetano's system, through new development plans, modernized aspects of the agricultural, industrial, and service sectors and linked reform in education with plans for social change. It also introduced cadres of forward-looking technocrats at various levels. The general motto of Caetano's version of the Estado Novo was "Evolution with Continuity," but he was unable to solve the key problems, which were more political and social than economic. As the boom period went "bust" in 1973-74, and growth slowed greatly, it became clear that Caetano and his governing circle had no way out of the African wars and could find no easy compromise solution to the need to democratize Portugal's restive society. The economic background of the Revolution of 25 April 1974 was a severe energy shortage caused by the world energy crisis and Arab oil boycott, as well as high general inflation, increasing debts from the African wars, and a weakening currency. While the regime prescribed greater Portuguese investment in Africa, in fact Portuguese businesses were increasingly investing outside of the escudo area in Western Europe and the United States.During the two years of political and social turmoil following the Revolution of 25 April 1974, the economy weakened. Production, income, reserves, and annual growth fell drastically during 1974-76. Amidst labor-management conflict, there was a burst of strikes, and income and productivity plummeted. Ironically, one factor that cushioned the economic impact of the revolution was the significant gold reserve supply that the Estado Novo had accumulated, principally during Salazar's years. Another factor was emigration from Portugal and the former colonies in Africa, which to a degree reduced pressures for employment. The sudden infusion of more than 600,000 refugees from Africa did increase the unemployment rate, which in 1975 was 10-15 percent. But, by 1990, the unemployment rate was down to about 5-6 percent.After 1985, Portugal's economy experienced high growth rates again, which averaged 4-5 percent through 1992. Substantial economic assistance from the EEC and individual countries such as the United States, as well as the political stability and administrative continuity that derived from majority Social Democratic Party (PSD) governments starting in mid-1987, supported new growth and development in the EEC's second poorest country. With rapid infrastruc-tural change and some unregulated development, Portugal's leaders harbored a justifiable concern that a fragile environment and ecology were under new, unacceptable pressures. Among other improvements in the standard of living since 1974 was an increase in per capita income. By 1991, the average minimum monthly wage was about 40,000 escudos, and per capita income was about $5,000 per annum. By the end of the 20th century, despite continuing poverty at several levels in Portugal, Portugal's economy had made significant progress. In the space of 15 years, Portugal had halved the large gap in living standards between itself and the remainder of the EU. For example, when Portugal joined the EU in 1986, its GDP, in terms of purchasing power-parity, was only 53 percent of the EU average. By 2000, Portugal's GDP had reached 75 percent of the EU average, a considerable achievement. Whether Portugal could narrow this gap even further in a reasonable amount of time remained a sensitive question in Lisbon. Besides structural poverty and the fact that, in 2006, the EU largesse in structural funds (loans and grants) virtually ceased, a major challenge for Portugal's economy will be to reduce the size of the public sector (about 50 percent of GDP is in the central government) to increase productivity, attract outside investment, and diversify the economy. For Portugal's economic planners, the 21st century promises to be challenging. -
10 static
статика; статические свойства (напр. балансировки колеса); электростатические явления; помеха электростатического происхождения; атмосферные помехи; ухудшение; усугбление; II статический; стационарный; неподвижный- static aeroelasticity - static air pressure - static angle of friction - static arrester - static breakdown voltage - static breeze - static buffering - static characteristic - static charge - static charge meter - static check - static coefficient - static commutation - static compaction - static compensation - static compensator - static conditions - static connection seal - static contact - static control - static controller - static current - static discharge - static discharge protection - static disturbance - static dump - static elasticity - static electricity test - static electromechanical relay - static elimination - static eliminator - static equilibrium equation - static error - static exciter - static failure - static force - static frequency converter - static friction force - static friction in suspension - static fuel flow method - static high-voltage distribution - static imbalance - static inverter - static indentation method - static load rating - static-loaded tyre radius - static loading - static loading fixture - static loading stress - static lubrication - static mass balancing - static mass spectrometer - static measurements - static measuring force - static mode - static moment - static-moment calculation - static operating life test - static orifice - static overvoltage - static part - static pile driving resistance of soil - static potential - static power amplifier - static pressure - static pressure energy - static pressure gradient - static pressure profile - static pressure traverse - static protection device - static regime - static regulator - static relay - static relay with output contact - static roller - static safety factor - static scales - static seal - static spline - static spray scrubber - static spring deflection - static spring rate - static stability - static stator - static steady-state instability - static steering torque - static stiffness - static strength - static stress - static suction head - static suction lift - static switch - static time delay - static tipping load rating - static toe-in - static toe-out - static torque - static torque-vs-angular-displacement curve - static-type plow - static tyre deflection - static tyre rate - static unbalance - static-weight roller - coefficient of static friction - datum statics - lightning static - man-made statics - precipitation static - residual statics -
11 lateral
1) трубный отвод
2) боковой
3) поперечный
4) побочный
5) второстепенный
– lateral acceleration
– lateral accelerometer
– lateral amplifier
– lateral area
– lateral axis
– lateral bending
– lateral deviation
– lateral face
– lateral flexure
– lateral instability
– lateral lantern
– lateral length
– lateral lobe
– lateral logging
– lateral magnification
– lateral micrologging
– lateral motion
– lateral nozzle
– lateral oscillations
– lateral pickup
– lateral recording
– lateral ridge
– lateral rigidity
– lateral separation
– lateral shear
– lateral spread
– lateral stability
– lateral thrust
– lateral tilt
– lateral truss
– lateral wave
– lateral working
lateral control of airplane — поперечное управление самолетом
resistance to lateral bending — сопротивление продольному изгибу
-
12 longitudinal
1) продольный
2) долготный
3) долевой
4) осевой
– longitudinal axis
– longitudinal beam
– longitudinal bulkhead
– longitudinal crack
– longitudinal curl
– longitudinal elasticity
– longitudinal flow
– longitudinal instability
– longitudinal lantern
– longitudinal magnetization
– longitudinal mass
– longitudinal member
– longitudinal metacenter
– longitudinal motion
– longitudinal oscillations
– longitudinal record
– longitudinal recording
– longitudinal shear
– longitudinal slot
– longitudinal stability
– longitudinal strain
– longitudinal strength
– longitudinal tie
– longitudinal tilt
– longitudinal wave
– longitudinal welding
longitudinal chromatic aberration — <opt.> хроматизм положения
-
13 hydrodynamic
-
14 limit
1. предел; граница; ограничение/ предельный; граничный/ ограничивать; задавать предел2. допуск3. ограничитель; упор1-g AOA limitacceleration limitactuator limitsaft CG limitaft CG stability limitair start limitall-attitude limitsaltitude limitangle-of-attack limitAOA limitauthority limitautothrust control limitbalance limitbank limitblowout limitbuffet limitbuzz limitCat I limitclosure limitcommand limitcontrol limitdeck lift-dictated limitdeflection limitdurability limitendurance limitengine installation limitexcursion limitfatigue limitfield of view limitsflaps-up limitflat-rated limitflight limitflying limitforward c.g. limitG limitg-rate limitgearbox limithandling limithazard limitHUD limitsincidence limitinstability limitlevel limitlife limitlift limitload factor limitMach number limitmaneuver limitmaneuvering limitmaximum angle-of-attack limitmaximum g limitmotivator operating limitsnozzle limitnozzle vectoring limitoff-axis limitoff-boresight limitone-sided limitsoverstressing limitpitch limitpitch trim limitpitch attitude limitpressure limitpressure suit limitsafety limitsaturation limitsideslip limitspeed limitstability limitstall limitstructural limittail-down limittail-up limittemperature limittolerance limittorsion limittorsional limittrim limitup-elevator authority limitusable limitwind limit
См. также в других словарях:
Modulational instability — In the field of nonlinear optics, modulational instability is a phenomenon whereby deviations from an optical waveform are reinforced by nonlinearity, leading to the generation of spectral sidebands and the eventual breakup of the waveform into a … Wikipedia
Power factor — For other uses, see Power factor (pistol). The power factor of an AC electric power system is defined as the ratio of the real power flowing to the load over the apparent power in the circuit,[1][2] and is a dimensionless number between 0 and 1… … Wikipedia
Microsatellite instability — Microsatellites are repeated sequences of DNA. Although the length of these microsatellites is highly variable from person to person, each individual has microsatellites of a set length. These repeated sequences are common, and normal. The most… … Wikipedia
Ribosome Recycling Factor — protein Name = mitochondrial ribosome recycling factor caption = width = HGNCid = 7234 Symbol = MRRF AltSymbols = EntrezGene = 92399 OMIM = 604602 RefSeq = NM 138777 UniProt = Q96E11 PDB = ECnumber = Chromosome = 9 Arm = q Band = 32… … Wikipedia
Political Instability Task Force — (formerly known as State Failure Task Force) was a U.S. government sponsored research project to build a database on major domestic political conflicts leading to state failures. The project was begun as an unclassified study that was… … Wikipedia
Landslide mitigation — Landslides can be triggered by many often concomitant causes. In addition to shallow erosion or reduction of shear strength caused by seasonal rainfall, causes triggered by anthropic activities such as adding excessive weight above the slope,… … Wikipedia
коэффициент нестабильности — — [Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.] Тематики электротехника, основные понятия EN instability factor … Справочник технического переводчика
коэффициент нестабильности индуктивности катушки — коэффициент нестабильности индуктивности Отношение изменения индуктивности к произведению квадрата индуктивности в начальный период времени и логарифма отношения времен, за которые произошло это изменение. где L1 индуктивность в начале периода… … Справочник технического переводчика
коэффициент нестабильности магнитной величины — Отношение нестабильности магнитной величины к начальному значению магнитной величины, измеренному до воздействия механических, климатических и других внешних факторов. [ГОСТ 19693 74] Тематики материалы магнитные EN instability factor DE… … Справочник технического переводчика
коэффициент нестабильности усиления (по накачке) — Отношение относительного изменения коэффициента усиления квантового парамагнитного усилителя к соответствующему относительному изменению мощности накачки. [Сборник рекомендуемых терминов. Выпуск 75. Квантовая электроника. Академия наук СССР.… … Справочник технического переводчика
Economic Affairs — ▪ 2006 Introduction In 2005 rising U.S. deficits, tight monetary policies, and higher oil prices triggered by hurricane damage in the Gulf of Mexico were moderating influences on the world economy and on U.S. stock markets, but some other… … Universalium